EPC in RFID Tags Explained: Boost Tracking Accuracy & Efficiency
Introduction
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) has become a cornerstone of modern industries, enabling businesses to track assets, manage inventory, and streamline operations without manual intervention. From retail shelves to hospital supply rooms, RFID tags are everywhere.

But here’s the challenge: accuracy and efficiency. In supply chains, retail, manufacturing, and healthcare, even a small error in tracking can lead to lost revenue, compliance issues, or safety risks.
This is where the Electronic Product Code (EPC) comes in. EPC transforms RFID from a simple identification tool into a powerful system for item-level tracking and intelligent data sharing, ensuring every product is uniquely recognized across the globe.
What is EPC in RFID?
The Electronic Product Code (EPC) is a universal identifier designed to give every physical object a unique digital identity. Think of it as a digital fingerprint for products.
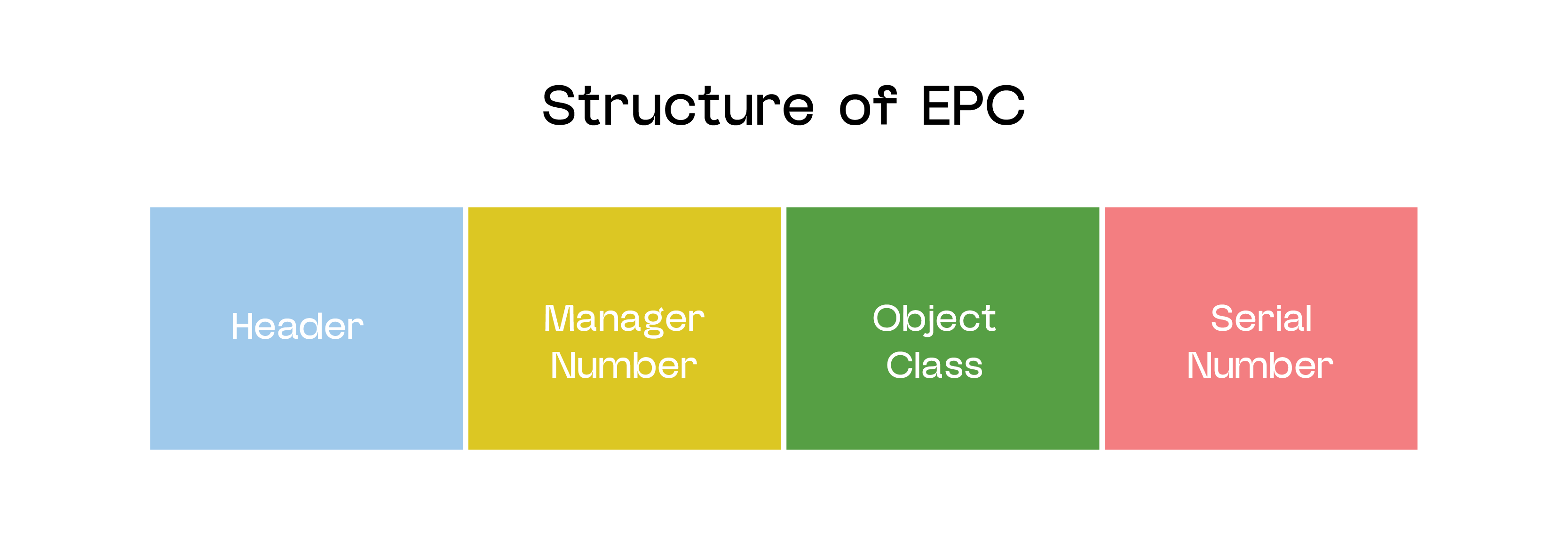
Structure of EPC
An EPC is made up of four key parts:
- Header: Defines which EPC scheme is applied, guiding how the code is interpreted across systems.
- Manager Number: Identifies the company or organization responsible for assigning and managing the product’s EPC identity.
- Object Class: Specifies the product type or category, such as a particular model or variation of an item.
- Serial Number: Provides item-level uniqueness, distinguishing one product from another even within the same object class.
Standards Governing EPC
EPC is primarily governed by standards developed by GS1 and EPCglobal organizations that set international standards for product identification and supply chain interoperability.
How EPC Works in RFID Tags
EPC-enabled RFID tags store the EPC code in their memory. Here’s how it works step by step:
Encoding
The EPC is programmed into the RFID tag during manufacturing, ensuring every item receives a unique digital identity for accurate tracking.
Reading
An RFID reader scans the tag wirelessly, capturing EPC data without requiring line-of-sight, enabling fast and efficient identification of multiple items simultaneously.
Middleware Processing
Captured EPC data is sent to middleware software, which filters out duplicates, corrects errors, and ensures only clean, reliable information moves forward.
Database Integration
The EPC data is matched with product records in databases, linking each tag to detailed information such as item type, batch, and location.
EPCIS (EPC Information Services)
EPCIS enables secure sharing of EPC data across supply chain partners, providing real-time visibility and standardized communication for global interoperability.
Real-World Example
Imagine a clothing retailer managing thousands of garments:
- At the factory: Each shirt, dress, or pair of jeans is assigned a unique EPC, ensuring item-level identification right from production.
- During shipping: RFID readers scan cartons and pallets, verifying EPCs to confirm the correct clothing items are loaded and reducing shipping errors.
- At the retailer’s store: EPC-enabled RFID tags allow staff to perform quick, accurate stock counts, track items across shelves and fitting rooms, and prevent counterfeit products from entering inventory.
- For customers: This system ensures the right sizes and styles are available, improving shopping experiences and reducing out-of-stock issues.
Benefits of EPC in RFID Tags
Enhanced Tracking Accuracy
EPC assigns a unique identity to every item, ensuring precise recognition across the supply chain. This eliminates duplication errors and reduces misreads, allowing businesses to track products confidently. Accurate identification improves inventory reliability, prevents mix-ups, and strengthens overall operational control.
Operational Efficiency
With EPC-enabled RFID, inventory counts become faster and more reliable. Staff can scan hundreds of items simultaneously without manual effort. Automated data capture at checkpoints reduces human error, speeds up workflows, and ensures smoother movement of goods from production to retail shelves, saving time and resources.
Global Standardization
EPC is governed by GS1 standards, ensuring interoperability across industries and countries. This global framework allows businesses to share product data seamlessly with partners worldwide. Standardization simplifies integration, supports compliance, and ensures that EPC-enabled RFID systems work consistently across diverse supply chains and geographic regions.
Data-Driven Insights
EPC provides real-time visibility into product movement, enabling businesses to monitor inventory and shipments instantly. Integrated with ERP, WMS, and analytics platforms, EPC data supports smarter decision-making. Companies gain actionable insights into demand, stock levels, and supply chain performance, helping them optimize operations and improve customer satisfaction.
EPC vs Traditional Identification Methods
|
Feature |
Barcodes |
Basic RFID |
EPC-enabled RFID |
|
Identification |
Product type only |
Limited unique IDs |
Item-level unique IDs |
|
Readability |
Line-of-sight |
No line-of-sight |
No line-of-sight |
|
Data Sharing |
Limited |
Proprietary |
Standardized EPCIS |
Applications of EPC in Different Industries
Retail
EPC-enabled RFID helps retailers maintain accurate inventory by uniquely identifying each clothing item or product. It reduces theft, supports faster stock counts, and enables seamless omnichannel fulfilment, ensuring customers find the right products both in-store and online.
Manufacturing
Manufacturers use EPC to track components throughout production, ensuring quality control and reducing errors. It helps manage assets, monitor work-in-progress, and streamline assembly processes, resulting in improved efficiency, reduced waste, and better visibility across the entire manufacturing cycle.
Logistics
In logistics, EPC verifies shipments at every checkpoint, reducing errors and delays. It streamlines cross-docking operations, improves route optimization, and ensures real-time visibility of goods in transit, helping companies deliver products faster and more reliably to customers.
Healthcare
Healthcare providers rely on EPC to track medical supplies, pharmaceuticals, and equipment. It ensures patient safety by preventing counterfeit drugs, supports compliance with regulations, and improves efficiency in managing hospital inventories and critical life-saving resources.
Waste Management
EPC supports waste management by monitoring waste streams and tracking recyclable materials. It ensures regulatory compliance, improves accountability, and helps organizations manage disposal processes more efficiently, contributing to sustainability and environmental responsibility.
Conclusion
The Electronic Product Code (EPC) elevates RFID from a basic identification tool to a global standard for intelligent tracking. By enabling item-level uniqueness, EPC boosts accuracy, efficiency, and visibility across industries.
For businesses, adopting EPC-enabled RFID is no longer optional—it’s a strategic move to stay competitive, compliant, and future-ready. As supply chains become smarter and more connected, EPC will remain the backbone of intelligent, efficient, and sustainable operations.
Recent Posts
-
RFID vs Barcode in Retail: A Side-by-Side Comparison
Introduction Retail is transforming at a rapid pace, and at the center of this change lies inventory …Mar 6th 2026 -
What Is an RFID Self-Checkout System? A Complete Guide for Retailers
Introduction Retail checkout has seen a remarkable transformation over the years. What started with …Feb 27th 2026 -
Upgrade from Barcodes to RFID on Shopify: A Retailer’s Guide
Retailers on Shopify are beginning to question whether barcodes are enough. With rising customer exp …Feb 24th 2026




