RFID Tag in Tire Identification and Tracking Applications
Introduction
In the modern automotive industry, where precision, safety, and efficiency are non-negotiable, the way businesses track and manage tires is undergoing a significant shift. Traditionally, tire tracking has been handled through barcodes, paperwork, and manual data entry—methods prone to human error, misplacement, and inefficiencies. For transport and logistics firms and the tire rental business model, this has often meant challenges such as incorrect tire installations, difficulty in getting information on tire life cycle, lack of data to manage fleets more efficiently, struggle to monitor tire performance and wear, and lack of visibility.
The integration of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology addresses these issues head-on. By attaching RFID tags directly to tires, businesses gain real-time, contactless visibility into each tire’s identity and journey. RFID tire tags bring automated accuracy to a once manual process, reduce errors, allow data-driven decision-making, and also prevent any potential malpractice.
In short, where traditional processes often created bottlenecks, RFID enables seamless, intelligent, and traceable tire management, turning a common pain point into a streamlined advantage.
What Are RFID Tire Tags?
RFID tire tags are compact transponders that carry unique identification data and are affixed to or embedded within the tire structure. Unlike traditional labels or barcodes, these tags do not require visual contact to be read, enabling seamless tracking even when the tire is in use.
There are two primary variants:
- Embedded tags, inserted during the tire’s manufacturing process, become a permanent fixture inside the rubber matrix.
- Patch tags, typically affixed post-production, are attached using vulcanized glue for a permanent bond with the tyre.
The majority of tire RFID applications utilize Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) passive tags. These tags harvest energy from RFID readers to transmit their data, making them both cost-effective and durable under intense thermal, pressure, and mechanical conditions inherent to automotive environments.
Why RFID for Tire Tracking? (Advantages Over Barcodes or Manual Processes)
RFID technology provides a paradigm shift over legacy identification methods. One of its most salient advantages is non-line-of-sight scanning, which enables bulk reading of tires stacked in warehouses or loaded on pallets without individual handling.
Its resilience to harsh environmental conditions—including high temperatures during curing, exposure to moisture, and road-induced abrasion—makes RFID suitable for the dynamic life of a tire.
The system’s ability to deliver instantaneous and precise data capture ensures that information related to model, batch, manufacture date, and usage history is readily accessible. Each tag contains a globally unique serial identifier, creating a digital fingerprint for every tire.
Furthermore, RFID’s tamper resistance and capacity to securely store critical data fortify the tire against counterfeiting and loss of provenance, issues particularly troubling in secondary markets and global logistics.
Benefits of Using RFID Tire Tags
RFID tire tags offer multilayered advantages to fleet operators, tire rental businesses and service centers alike. First and foremost, they enable end-to-end visibility across the entire tire lifecycle, right from the installation to final disposal.
With increased automation and efficiency, manual scanning, human error, and paperwork are dramatically reduced, optimizing workflows and operational throughput.
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology offers significant benefits in tire rental models by enabling efficient tracking, management, and maintenance of tires throughout their lifecycle
Most importantly, the wealth of operational data generated empowers stakeholders to make informed, data-driven decisions, improving predictive maintenance, minimizing downtime, and maximizing return on investment (ROI).
Applications of RFID Tire Tags
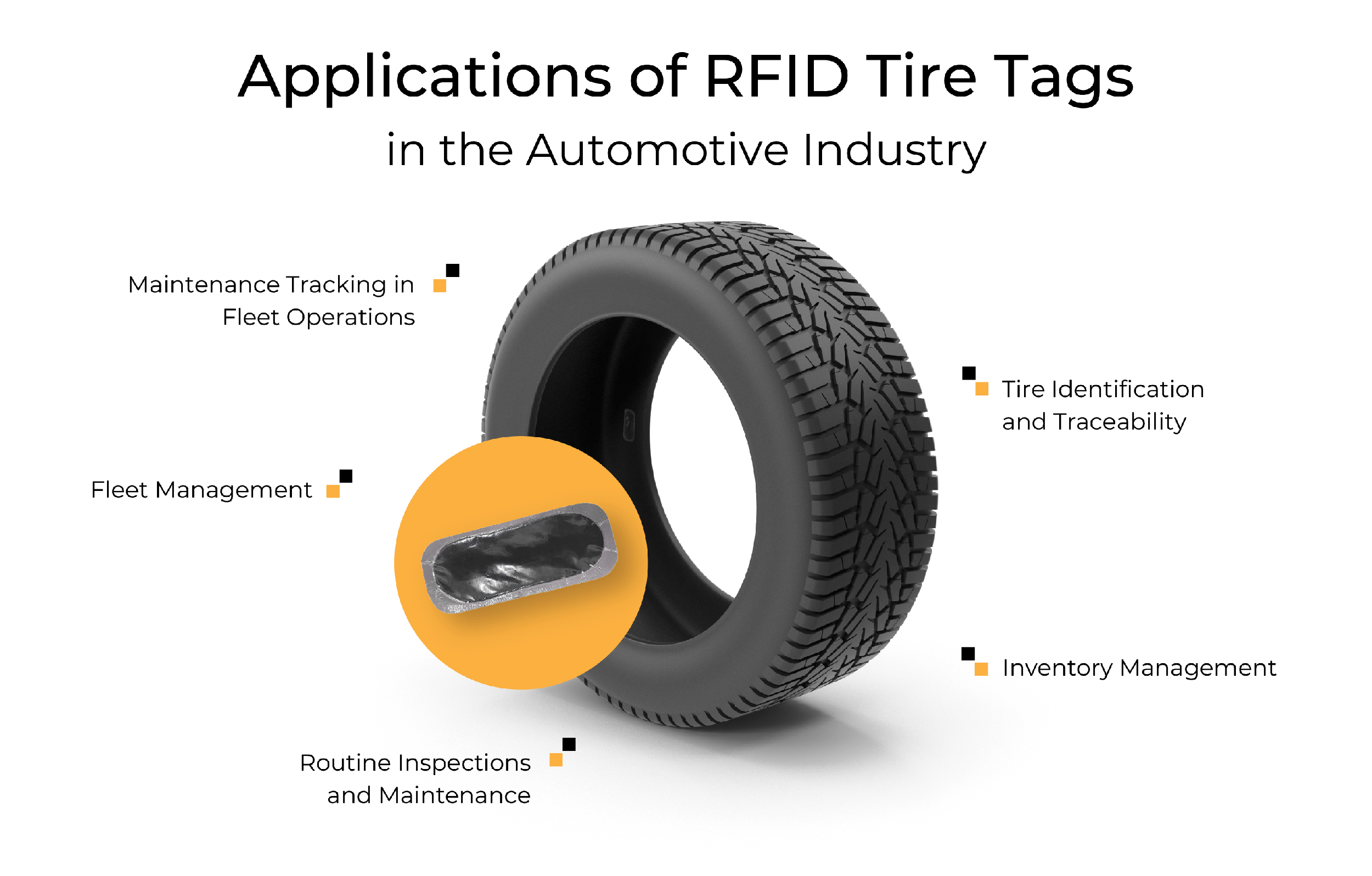
Tire Identification and Traceability
Each RFID tire tag carries a unique ID, making it possible to track a tire’s full history—from installation to end-of-life. This ensures traceability and helps verify authenticity
RFID tire tags help prevent malpractice by providing unique, trackable identification for each tire, making it difficult to swap, tamper with, or mismanage tires.
Inventory Management
RFID enables automated inventory of tires in stock without needing line-of-sight. It reduces errors, accelerates audits, and provides real-time stock visibility, ensuring that tire supply meets demand without unnecessary overstock or shortages.
Routine Inspections and Maintenance
During scheduled inspections, RFID allows technicians to instantly identify tires and retrieve inspection logs. It ensures adherence to maintenance protocols, enables predictive servicing based on wear patterns, and removes the guesswork from routine tire evaluations across fleets or service networks.
Fleet Management
RFID tags attached to vehicles allow for automated identification and monitoring of vehicle status and maintenance schedules. This leads to improved operational efficiency, enhanced security, reduced costs, and better overall fleet management.
RFID facilitates automated check-in and check-out processes for vehicles in a fleet and help to streamline the management of vehicle movements
Maintenance Tracking in Fleet Operations
Large fleets benefit immensely from RFID-enabled tire lifecycle monitoring. Each tire can be tracked for usage metrics such as mileage, pressure history, and retread cycles, minimizing tire-related failures.
Fleet managers can detect tire swaps, theft, or mismatches, thus reducing liability and ensuring vehicle integrity. The outcome is a safer, more cost-efficient, and data-governed maintenance program.
How to Attach RFID Patch-Type Tags to Tires – Step-by-Step Process
Attaching RFID patch-type tags to tires is a precise and standardized process, typically performed after the tire has been manufactured. Unlike embedded tags, these are externally applied to the tire’s inner surface using vulcanized glue/cement designed to withstand heat, friction, and environmental exposure. Below is the step-by-step procedure for applying patch-type RFID tags to tires:

Step 1: Select the Tag Placement Area
- Choose a flat, smooth section on the inner liner of the tire, typically away from tread belts and flex zones.
- This location should offer minimal stress during tire operation to maintain the integrity of the tag.
- Avoid areas near the bead or areas exposed to direct contact with the rim or mounting equipment.
Step 2: Prepare the Tire Surface
- Clean the inner liner of the tire thoroughly to remove any dust, oils, or mold-release agents.
- Use a suitable cleaning agent or alcohol-based solvent to ensure the surface is free from contaminants.
- Let the area dry completely before proceeding.
- Using sandpaper or a scuffer tool, roughen the surface This creates a better surface for the glue to adhere to the tire.
Step 3: Apply the Adhesive or Activator
- Apply a thin, even layer of rubber cement or vulcanizing glue to the roughened area, ensuring the glued area is slightly larger than the patch.
- Allow the glue to dry until it is tacky to the touch.
Step 4: Attach the RFID Patch Tag
- Carefully remove the backing from the patch, handling it only by the edges.
- Carefully place the tag onto the prepared section of the tire.
- Press firmly and evenly to ensure full contact between the patch and the tire surface.
- Use a roller or hand tool to remove air bubbles and secure the bond.
Step 5: Allow Curing Time
- Let the adhesive cure as per the manufacturer's instructions—this may range from a few minutes to several hours.
- Avoid moving or mounting the tire until the curing process is complete to prevent misalignment or detachment.
Step 6: Verify Tag Functionality
- Once cured, scan the RFID tag using a compatible reader to verify it has been properly installed and is functioning.
- Record the tag’s unique ID and link it to the corresponding tire data in the system.
Patch-type RFID tags provide a reliable and cost-effective solution for tire identification, especially in aftermarket applications, warehouses, and maintenance facilities. When applied correctly, they enable efficient tire tracking without altering the tire’s structural integrity.
Conclusion
RFID tire tags are revolutionizing how the industry perceives and manages tires intelligently. From production traceability to post-sale service optimization, RFID is not just a tool—it's a strategic asset.
In an industry rapidly moving toward automation, electrification, and sustainability, RFID technology supports a vision of connected, traceable mobility. Its value extends beyond tracking; it fosters safety, transparency, and operational excellence.
Adopting RFID tire tags is not merely a technological upgrade—it’s a forward-thinking investment into the future of mobility, logistics, and customer satisfaction.
Recent Posts
-
What Is an RFID Self-Checkout System? A Complete Guide for Retailers
Introduction Retail checkout has seen a remarkable transformation over the years. What started with …Feb 27th 2026 -
Upgrade from Barcodes to RFID on Shopify: A Retailer’s Guide
Retailers on Shopify are beginning to question whether barcodes are enough. With rising customer exp …Feb 24th 2026 -
Work-in-Progress Tracking with RFID in Manufacturing
Introduction In manufacturing, Work-in-Progress (WIP) refers to items that are in various stages of …Feb 20th 2026